Parts of a Washing Machine – Brief Guide
Washing machines have different parts and it is essential to understand each one of their function. Understanding the parts can help us do repair and maintenance on our own.
Therefore, in this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various parts that make up a washing machine. Also, we will explore their roles and functions.

Parts of a Washing Machine
A typical washing machine consists of 11 major parts. These parts aid in the functioning of a washing machine.
- Outer Cabinet
- Inner Tub
- Agitator or Impeller
- Motor and Transmission
- Water Inlet Valve
- Detergent Dispenser
- Lid or Door
- Control Panel and User Interface
- Sensors
- Drain Pump
- Heating Element (On selected models)
Outer Cabinet

The outer cabinet of a washing machine is its protective shell. The outer shell provides structural integrity and aesthetics to the entire washing machine.
Typically, the outer cabinet has a plastic body. The plastic body prevents corrosion and provides long life to the outer structure.
The cabinet is responsible for holding the inner tub and all the other components of the washing machine.
Apart from structure, the outer cabinet also contributes to noise insulation. Noise insulation helps in minimizing the noise during the washing and spinning cycles.
Inner Tub

The inner tub of the washing machine is designed to hold your clothes during washing.
The tub is constructed from materials resistant to corrosion, such as stainless steel and plastic. Some tubs also have porcelain coating to resist corrosion. The inner tub is built to withstand repeated exposure to water and detergents.
The tub has a unique design with perforations or holes. This design allows water and detergent to circulate freely, ensuring efficient cleaning of your laundry.
The inner tub can spin with the help of the motor and transmission present in the washing machine. The tub circulates the clothes along with water and detergent during a wash cycle.
Agitator or Impeller
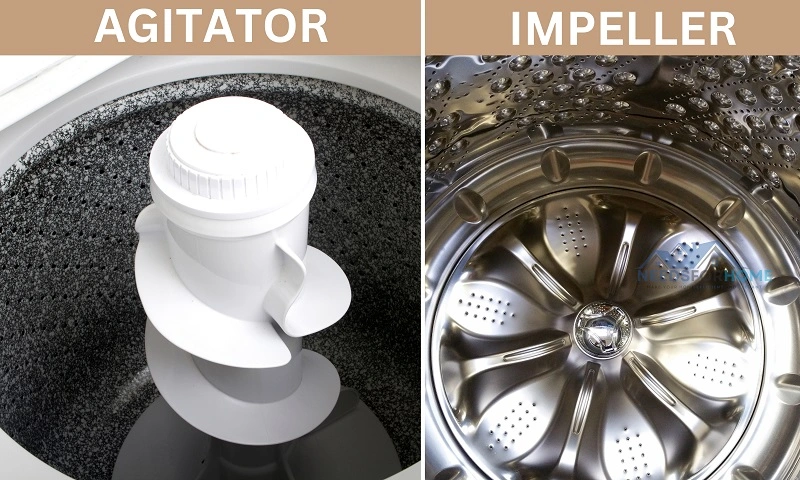

The agitator is the part responsible for agitating your clothes during the washing cycle. Different washing machines employ varying mechanisms for this purpose.
In traditional top-load washing machines, you will have an agitator or an impeller. An agitator is a spindle with fins or paddles. The agitator moves the clothes around the tub and facilitates the cleaning process.
In some top-load washing machines, you can find an impeller. The impeller is a low-profile cone or fin fixed to the inner tub’s bottom.
Front-load washing machines use a drum that rotates horizontally. The drum has special fins to tumble the clothes around while washing.
Washing machines with agitators require more water to tumble the clothes against each other. Whereas, washing machines with impellers can agitate the clothes with very less water. Front-loading machines also use less water due to the drum with fins setup.
Motor and Transmission
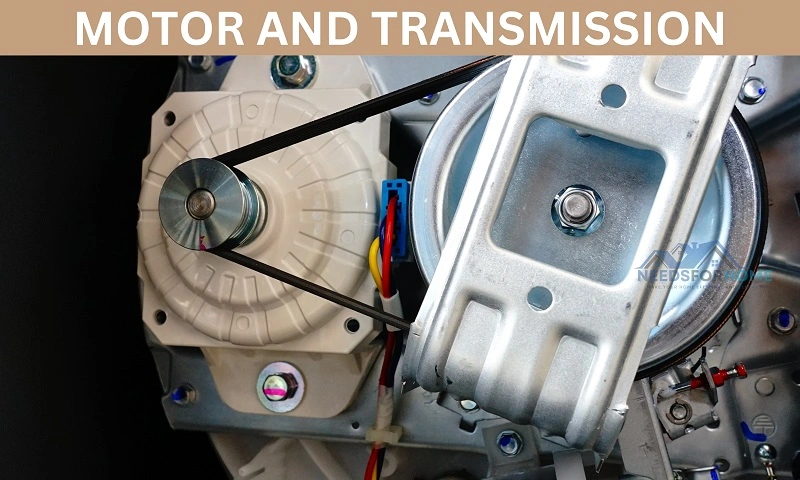
The motor of a washing machine provides the necessary energy to drive the tub or drum.
Washing machines employ various motors, including traditional brushed motors, induction motors, and Brushless DC (BLDC) motors. These motors come in different sizes and power ratings, affecting the machine’s overall performance.
The most commonly used motor is the induction motor. It offers better efficiency and speed control. Modern washing machines use BLDC motors to reduce noise during operation and to lower power consumption.
The motor is connected to the inner tub through two different drives according to the model of the washing machine. The drives are:
- Direct Drive
- Belt Drive
In the direct drive mechanism, the motor is connected directly to the inner tub of the washing machine through a shaft.
In the belt drive mechanism, the motor output shaft is connected to a transmission through a belt. This transmission is connected to the inner tub of the washing machine.
The transmission in a washing machine helps in transferring power from the motor to the tub or drum. It ensures that the rotational motion generated by the motor is appropriately transmitted to the inner tub that is holding the clothes.
The transmission system has a set of gears to aid the agitation, spin, and other wash cycles present in the washing machine.
Water Inlet Valve

The water inlet valve is situated at the back of the washing machine. It controls the flow of water into the appliance. There are separate connections for hot and cold water sources.
The presence of hot and cold water sources allows the washing machine to choose the temperature for different wash cycles.
Different sensors and control valves operate the water inlet valve to ensure precise water flow into the washing machine tub.
Detergent Dispenser
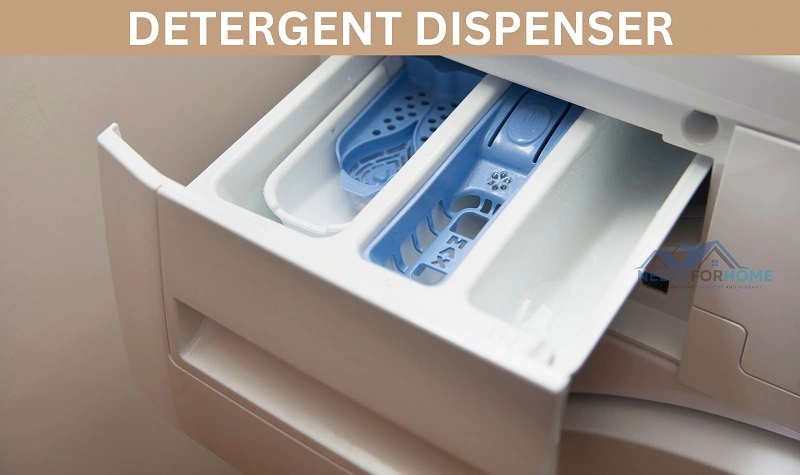

The detergent dispenser is a dedicated compartment within the washing machine. It is the compartment where you place detergent before starting a wash cycle.
Washing machines come with two types of detergent dispensers. They are:
- Automatic Dispenser
- Direct Dispensing
In automatic dispensers, you have a drawer in the washing machine to pour the detergent. During the wash cycle, the machine automatically dispenses the detergent from the drawer. This type of dispensing is found in front-load washers.
In direct detergent dispensing, you have to pour the detergent directly into the tub before the initiation of the wash cycle. This type of dispensing is done in top-load washers.
Understanding the type of dispenser in your machine is essential for proper detergent usage. Because it influences when and how detergent is introduced into the wash cycle.
Lid or Door

The lid or door of a washing machine serves as the entry point for loading and unloading your laundry. Washing machines feature either a lid or a door depending on their design.
Top-loading machines have hinged lids that open upward, providing easy access to the inner tub.
Front-loading machines feature a sealed door at the front, which swings open to allow access.
Both the lid and door are equipped with a safety lock to prevent accidental access to the washer tub during a wash cycle. All the washing machine models have a switch and lock mechanism to prevent the opening of the lid or door during a wash cycle.
Proper maintenance and adherence to safety guidelines are essential to prevent accidents when using the lid or door.
Control Panel and User Interface

The control panel and user interface of a washing machine help you to customize your laundry experience. It houses an array of features, buttons, and dials that allow you to program and select washing cycles based on your specific needs.
The complexity of the control panel can vary from basic models with simple mechanical knobs to high-end digital displays and touch-sensitive controls.
The control panel is connected to the motor and transmission to actuate the selected wash cycles. Also, the control panel gets feedback from the different sensors to initiate wash cycles, spin cycles, control water flow, pause the wash cycle, etc.
Technological advancements have brought innovations like Wi-Fi connectivity and smartphone app control, providing convenience and flexibility in operating your washing machine.
Sensors
Sensors are an integral part of a washing machine. Especially in modern automatic washing machines, the complete washing mechanism depends on the sensor’s feedback.
Sensors in a washing machine aid in the following activities:
- Sensors help in sensing the overall load present in the washing machine.
- They can help in controlling the water inlet according to the wash cycle chosen by the user.
- Sensors provide feedback to the control panel to initiate the wash cycle.
- The motor speed is monitored with the help of sensors. They provide feedback to the motor’s control unit to achieve the proper speed according to the wash cycle.
- Sensors also help in lid lock or door lock mechanisms.
- Some washing machines have temperature sensors to monitor the water temperature.
- Modern sensors can also feedback on the pressure and vibration of the tub to notify the need for maintenance.
Drain Pump

Once the washing cycle is complete, the washing machine must efficiently remove water to prepare the clothes for drying. This is where the drain pump comes into play.
The drain pump is responsible for expelling the used water from the machine, ensuring that your clothes are left as dry as possible after the wash. The drain pump assembly has a small motor to pump out the dirty water from the inner tub.
Various types of drain pumps with different flow rates and capacities are used in washing machines according to the model.
Regular maintenance and occasional troubleshooting are essential to keep the drain pump functioning optimally.
Heating Element
Modern washing machines have heating elements in select models to heat the inlet water. Some wash cycles require hot water. The heating element helps in heating the water and performing the wash cycle.
The heating element is combined with a temperature sensor to maintain the water temperature. This cannot be found in many models because in most washing machines there are separate valves for hot and cold water.
Why it is Necessary to Know the Parts of a Washing Machine?
Knowing the different parts of a washing machine can help you to effectively maintain and troubleshoot the appliance.
Most of the time, you can DIY the repair and maintenance of your washing machine if you know the parts and their working.
When you want to replace any part in your washing machine, knowing the parts can help you to order a replacement with ease.
If you know the parts involved in your washing machine, you can efficiently use the appliance and get the most out of it.
Do Different Washing Machine Models have Different Parts?
The parts we have listed are commonly found in all washing machine models. There can be additional features in high-end models but they are not integral to the basic working of the machine.
Only the parts we have mentioned above are responsible for the working of a washing machine. They are found in all types and models of washing machines.
The additional features of the machine can be found on the manufacturer’s website. Also, you can find them in the user manual provided with the washing machine.


